 NEW: BrowserGrow.com is now available!
AI agents to grow your business & do your marketing on autopilot in your browser
NEW: BrowserGrow.com is now available!
AI agents to grow your business & do your marketing on autopilot in your browser

 NEW: BrowserGrow.com is now available!
AI agents to grow your business & do your marketing on autopilot in your browser
NEW: BrowserGrow.com is now available!
AI agents to grow your business & do your marketing on autopilot in your browser

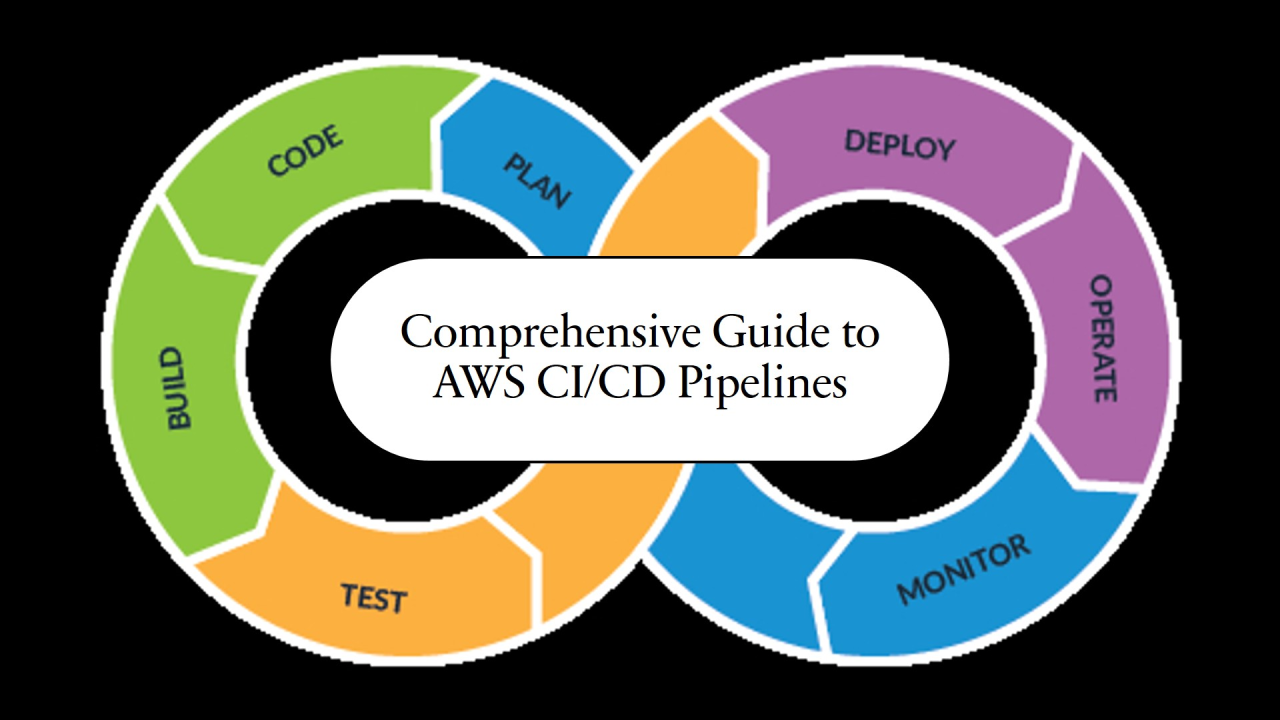
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are foundational practices in modern software development. They enable teams to deliver software faster, with fewer errors, and higher reliability. By automating code integration, testing, and deployment, developers can focus on building features rather than manually managing repetitive processes.
CI/CD is essential for teams aiming to improve collaboration, maintain code quality, and release updates quickly. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to implementing CI/CD pipelines for teams of any size.
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI focuses on integrating code changes frequently into a shared repository. Key practices include:
Frequent commits to version control
Automated builds triggered by commits
Running unit and integration tests automatically
Continuous Deployment / Delivery (CD)
CD automates the process of delivering changes to production or staging environments:
Continuous Delivery: automated deployments to staging environments, with manual approval for production
Continuous Deployment: fully automated deployment to production
Popular CI/CD tools include Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and Travis CI. For teams seeking expert guidance, a web development company can provide consulting and hands-on implementation services to set up CI/CD pipelines efficiently and securely.
Before building a pipeline, define the following:
Project requirements – What kind of application and environments?
Pipeline stages – Common stages include build, test, and deploy
Tool selection – Decide which CI/CD tools, testing frameworks, and deployment platforms to use
Success metrics – Examples: build time, deployment frequency, failure rates
Proper planning ensures that your pipeline scales with your team and application needs.
Version Control
Use a structured branching strategy (Gitflow or trunk-based development) for consistency.
Build Automation
Automate compilation, dependency management, and artifact generation.
Automated Testing
Include unit, integration, and end-to-end tests in the pipeline to catch issues early.
Artifact Management
Store build artifacts in a repository to maintain versioning and reproducibility.
Deployment
Deploy to multiple environments (dev, staging, production) with rollback or blue-green deployment strategies.
Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible to automate environment setup.
Containerize applications with Docker or Kubernetes for portability.
Consider cloud deployment options (AWS, Azure, GCP) for scalability and reliability.
VI. Monitoring and Feedback
Implement logging and monitoring to track application performance and pipeline health.
Set up alerts for build or deployment failures.
Use feedback loops to continuously improve the pipeline and development process.
VII. Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Keep pipelines fast and efficient to prevent bottlenecks.
Ensure security by scanning dependencies and managing secrets.
Avoid overcomplicating pipelines; simplicity improves maintainability.
Learn from real-world scenarios and iterate gradually.
VIII. Case Study / Example Pipeline
Example: A SaaS product pipeline includes:
Code pushed to Git repository triggers CI build.
Automated unit and integration tests run.
Successful builds create artifacts stored in an artifact repository.
Deployment to staging environment for manual QA.
After approval, deployment to production with monitoring enabled.
This setup ensures a smooth, repeatable process from code commit to live deployment.
IX. Conclusion
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline improves software delivery speed, quality, and reliability. Start small, automate the most critical stages first, and iterate. Over time, your pipeline will evolve into a robust system that accelerates development and enhances team collaboration.
For teams looking for professional assistance, companies like Techuz provide expert services to implement CI/CD pipelines tailored to your organization’s needs.